India’s commitment to environmental sustainability is gaining fresh momentum as wildlife conservation and eco-tourism continue to grow across states. The establishment of new wildlife sanctuaries, coupled with inter-state irrigation projects, is creating a balanced model of development that protects nature while supporting rural livelihoods.
Growing Focus on Eco-Tourism and Conservation
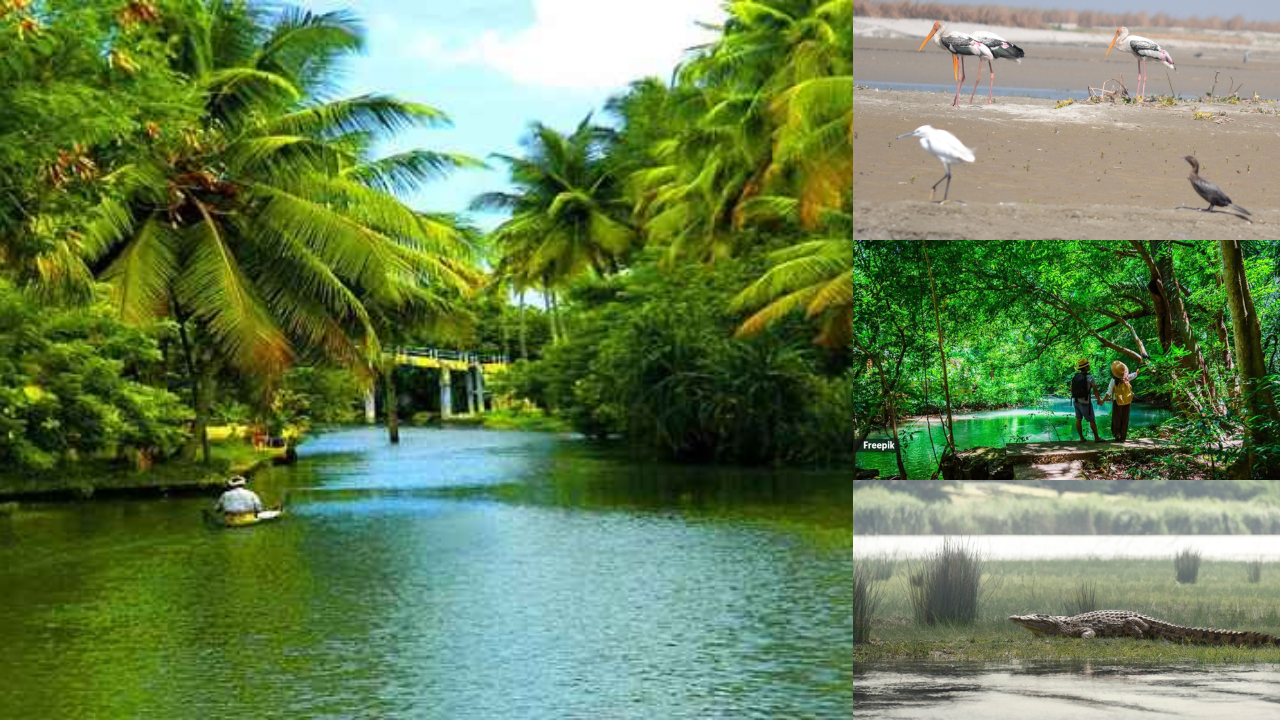
Over the past few years, India has witnessed a steady rise in eco-tourism — a form of travel that emphasizes environmental preservation and responsible exploration. This growth is not just about tourism but also about creating awareness of biodiversity and boosting local economies close to forested regions. Forest departments, wildlife boards, and tourism ministries across states like Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Rajasthan are introducing new initiatives to make nature accessible while ensuring conservation.
Officials highlight that eco-tourism is helping communities earn sustainable income without harming the environment. Tribal and rural populations living near protected areas are now becoming key stakeholders in the process. They are trained as forest guides, homestay operators, and craftsmen, helping preserve both cultural heritage and ecology.
New Wildlife Sanctuaries Strengthening Biodiversity
Several states are approving new wildlife sanctuaries and conservation areas to protect endangered species and improve green cover. The new sanctuaries serve as safe corridors for animals migrating between forest zones. In Madhya Pradesh, often referred to as the “Tiger State of India,” proposals for additional protected regions have been welcomed to maintain balance between humans and wildlife.
Similarly, Maharashtra’s forest department has been expanding its network of community reserves. These efforts are part of the state’s broader policy to promote eco-tourism in places like Tadoba, Pench, and Melghat, where visitor management and local employment play equal roles in sustainable growth.
Experts believe the creation of such sanctuaries will not only boost biodiversity but also help India achieve several of its commitments under the Global Biodiversity Framework. With new habitats being restored, the chances of human–wildlife conflict also reduce, creating a safer coexistence model.
Inter-State Irrigation Projects Enhancing Sustainability
Parallel to wildlife expansion, inter-state irrigation projects are playing a major role in India’s environmental strategy. These projects are improving water resource sharing and enhancing agricultural productivity while also rejuvenating local ecosystems. By ensuring equitable distribution of river water among states, such infrastructure projects reduce dependency on rain-fed agriculture and strengthen groundwater reserves.
One notable impact of these irrigation projects is their contribution to reforestation and soil conservation. Canal networks and water reservoirs often turn nearby zones into fertile green areas, indirectly supporting wildlife by maintaining natural habitats. States like Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra have collaborated on large-scale irrigation initiatives that aim to benefit both farming communities and local ecology.
Environmentalists note that by linking rivers and managing water flow more effectively, India is reducing the risk of droughts in arid regions and floods in catchment areas. Irrigation projects are no longer viewed as purely agricultural; they are becoming vital for maintaining ecological equilibrium.
Economic Benefits through Green Growth
Eco-tourism and sustainable irrigation together are redefining rural economies. The expansion of eco-parks, nature trails, and wildlife sanctuaries attracts domestic and international tourists, generating employment for local residents. From forest guides and conservation workers to small business owners in hospitality and transport, many rural families are directly benefiting.
Moreover, the government’s push for green development is attracting private investments in eco-friendly infrastructure. Several new resorts and camps near wildlife parks now follow eco-certifications, ensuring minimal waste and reduced carbon footprint. According to tourism departments, income from nature-based tourism contributes significantly to conservation funding, making the system self-sustaining.
In areas supported by irrigation projects, the rise in agricultural productivity boosts food security and rural income. When farmers have reliable water supply, they rely less on groundwater extraction and can diversify crop patterns. Combined with eco-tourism initiatives, these measures uplift entire rural regions while maintaining environmental balance.
Technological Support for Sustainability
The integration of technology is another key factor driving environmental progress. Satellite tracking, GIS mapping, and drone surveillance are improving wildlife monitoring and forest management. Similarly, advanced irrigation systems use sensors and automation to reduce water wastage. These innovations are helping the government and conservation agencies ensure transparency and efficiency.
Furthermore, digital platforms are promoting responsible tourism by providing real-time information about parks, visitor limits, and safety guidelines. Online ticketing and eco-tourism apps have made wildlife experiences more accessible while reducing paperwork and improving regulation.
Public Awareness and Community Role
Sustainability efforts cannot succeed without public involvement. Environmental campaigns, school programs, and local community drives are spreading awareness about protecting forests and using water judiciously. In many districts, eco clubs and youth volunteers organize tree-planting activities, clean-up drives, and awareness walks to support conservation messages.
Community-led initiatives have been particularly effective in protecting endangered species. In some forest regions, residents have voluntarily created patrol groups to prevent poaching and illegal logging. Their contribution highlights how grassroots participation can amplify large-scale policy impact.
The Road Ahead
India’s vision for sustainable growth lies in combining conservation with development. As wildlife sanctuaries expand and eco-tourism flourishes, the country is not only preserving its natural wealth but also building a greener economic future. Inter-state irrigation projects add an environmental dimension to infrastructure development, ensuring that progress benefits both people and the planet.
The continued collaboration among governments, communities, and environmental experts promises a balanced path forward. With steady policy support and rising public awareness, India’s model of eco-friendly growth can serve as an example for other nations seeking harmony between nature and development.