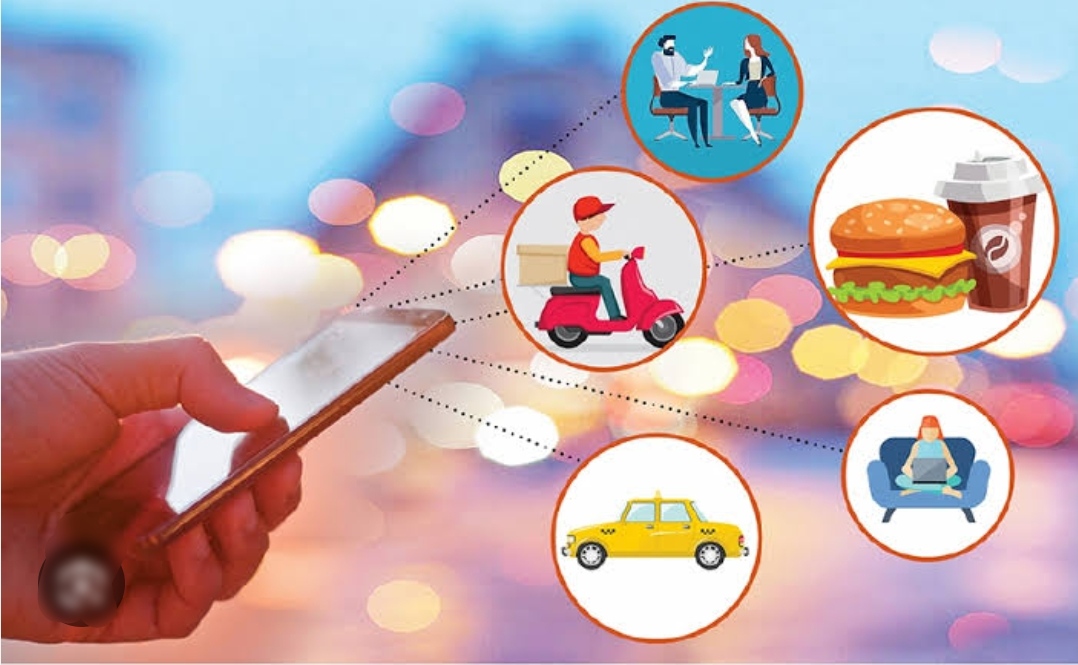
The rise of the gig economy, characterized by temporary, flexible, and freelance work arrangements, has reshaped traditional employment models and transformed the way people work and earn a living. This trend has been fueled by technological advancements, changing attitudes towards work-life balance, and economic factors driving both supply and demand for flexible labor.
One of the key trends within the gig economy is the proliferation of digital platforms connecting freelancers with clients seeking specific skills or services. These platforms, often referred to as “gig platforms” or “online marketplaces,” facilitate transactions between freelancers and clients, providing a convenient and efficient way to match supply and demand for freelance work.
The gig economy offers numerous benefits for both freelancers and clients. Freelancers enjoy greater autonomy and flexibility over their work schedules, allowing them to pursue multiple projects simultaneously, work remotely, and balance work with other commitments. Additionally, freelancers have the opportunity to diversify their skills and experiences by working with a variety of clients across different industries.
For clients, the gig economy provides access to a global talent pool, enabling them to find specialized skills and expertise on-demand without the overhead costs associated with traditional employment arrangements. This flexibility allows businesses to scale up or down quickly in response to changing market conditions, improve efficiency, and access a broader range of talent than may be available locally.
However, the rise of the gig economy also raises concerns and challenges, particularly regarding labor rights, job security, and income stability. Freelancers often lack access to benefits such as healthcare, retirement savings, and unemployment insurance traditionally provided by employers. Additionally, gig workers may face income volatility and uncertainty due to the unpredictable nature of freelance work and fluctuating demand for their services.
Furthermore, the gig economy has implications for traditional employment models and labor markets. Some critics argue that the proliferation of freelance work may contribute to the erosion of stable, full-time employment opportunities, exacerbate income inequality, and weaken labor protections. Others view the gig economy as a response to changing preferences and economic realities, offering individuals greater flexibility and opportunities for entrepreneurship.
In conclusion, the rise of the gig economy has reshaped the landscape of work, presenting both opportunities and challenges for freelancers, clients, and society at large. As the gig economy continues to evolve, policymakers, businesses, and workers alike must address the complexities and implications of this trend to ensure fair and equitable outcomes for all stakeholders involved.
For more information visit at https://happenrecently.com/zepto/?amp=1